Does chloride ion in the water used for hydrostatic test of titanium tube really matter?
In some inquiries or projects that our company received and worked, clients sometimes required that the chloride ion content of water for hydrostatic test shall be less than 25 ppm or 10 ppm. But does it really matter for titanium?
There’s article showing that actually it is only applicable for stainless steel, nickel and nickel alloy tube. According to GB 50235-2010 and GB 50184-2011, clean water shall be used in hydraulic tests.When testing stainless steel, nickel and nickel alloy pipes or pipes connected with stainless steel, nickel and nickel alloy pipes or equipment, the chloride ion content in water shall not exceed 25mg/L (25ppm).
Why is it not applicable for titanium? Because titanium has great character of anti-corrosion. The applicable standards ASME SB338 & ASTM B338 also don’t specify any requirement about water used for hydrostatic test.
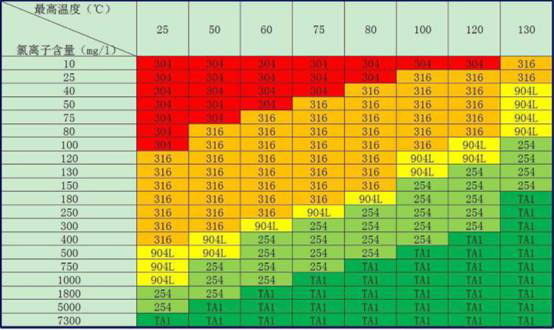
Below is a chart showing the chlorine-ion environments for stainless steel, super stainless steel, and titanium.
Red part is for low PPM and low temperature environment, conventional stainless steel 304, green part is for high temperature and high PPM environment, titanium TA1 which is Gr1/Gr2 shall be the priority for high temperature and high PPM environment.
As can be seen from the chart, chloride ion resistance has a simple arrangement:
304<316L<904L<254SMO<Non-alloy titanium
What is the performance of titanium’s resistance to chloride ion corrosion?
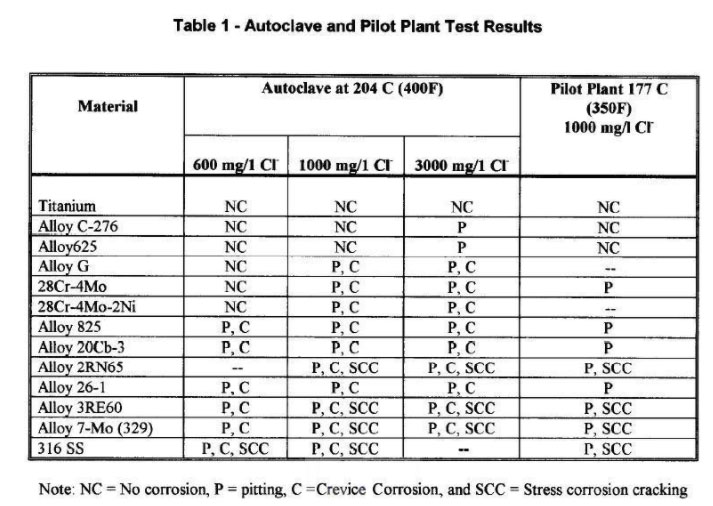
On the previous chart, the first line is titanium. It can be seen that when the C276 nickel-based alloy starts to corrode a little at 204 degrees and 3000ppm, the titanium is still fighting without any corrosion.
Titanium is known to be almost immune to chlorine-rich seawater and has little corrosion.
The salinity of seawater is usually less than 5%. According to long-term experiments and practical use, it is considered that pure titanium can be safely used in seawater below 120 degrees. However, crack corrosion may occur if the temperature continues to rise, and pitting corrosion may occur if the temperature continues to rise.
Ti- palladium (TI-0.2PD, Grade 7) and Ni - molybdenum (TI-Grade 12) can be used in pressurized sea water at 260 degrees!
The corrosion resistance results of pure titanium, titanium palladium alloy (Grade 7), titanium nickel molybdenum alloy (Grade 12) in sodium chloride solution and magnesium chloride solution of different concentrations are shown below.
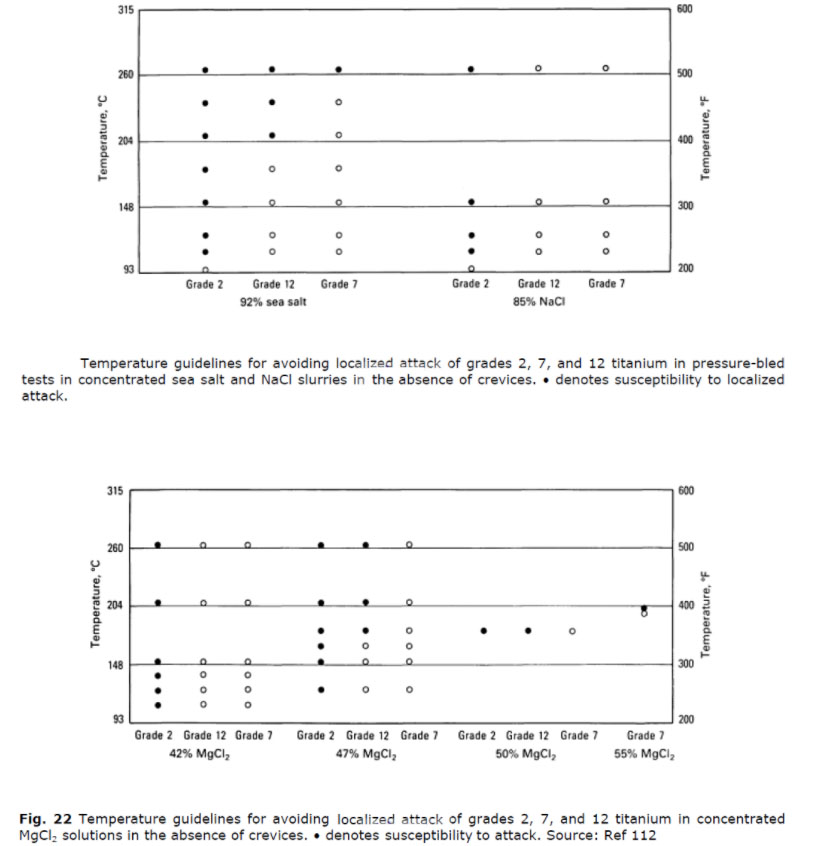
It can be seen that in this working condition, the degree of chloride ion resistance of ti - Pd alloy and Ti - Ni - Mo alloy is much higher than that of non-alloy titanium!
Corrosion resistance: Grade 7 >Grade 12 >Non-alloy titanium (Grade 2)
Note: The white circles in the picture represent usable. The black circle represents the vulnerability to crevice corrosion or pitting;White triangles represent slight crevice corrosion, but do not affect usage.
Disclaimer: The views expressed herein are just general point and do not apply for any certain project.




